Social Statics
According to Auguste Comte, social statics study social structure, its constituent parts, and their interactions in maintaining social order. Therefore, the study of current social situations as they are studied using a theory of social order is known as social statics.
Comte distinguished between social dynamics and social statics. Social statics examines the interactions between the constituent social structures that make up a social system and their functional connections to one another and the social system in general. Since family, language, religion, and the division of labor are all social phenomena that affect people collectively, Comte also concentrated his social statics on the individualistic level.
It is a framework for sociology that focuses on the distinctive features of societies and social systems in abstract instead of empirical terms. Social statics is an offshoot of social physics that interacts with the fundamental laws of the social order and the equilibrium of powers in a functional and stable society.
It is the examination of social structures in the given moment. It investigates human cultures as they are at a particular era and relative stage of development.
Three different social statics levels
Understanding social evolution requires knowledge of social statics. Social statics exist on three levels: individual, family, and society.
A. Individual
It is possible to learn about the nature of the idea of “man” if researchers assume certain things about it. To begin with, it is conceivable to develop a theory of human intelligence and morality from the standpoint of biology and as a species. One of a man’s most significant attributes is that emotions outweigh intellect. In general, people are not equal.
B. Family
In his opinion, the family is the social unit rather than the individual. A family grows into a tribe, which subsequently develops into a country. Monogamy is the default state of family life in human civilization, yet humans have reached this point by following polygyny or polyandry. The notion of the family depends on two factors. First, the institutionalized marriage system regulates the physical intimacy of interactions between men and women. The second is the bond between parents and children, which is how people learn to be disciplined.
C. Society
For Comte, functional specialization in society happens as if it were established law. However, interpersonal harmony is essential to society. Individual collaboration is at a low degree in a primitive civilization. With the growth of society, so does the degree of cooperation. Social statics are produced by the division of labor and employment, governmental structure, and other factors.
Comte’s concept of social statics vividly highlights the foundational ideas of sociology, which are still essential and up for debate today. The majority of influential sociologists begin by forming assumptions about people and society. Family is crucial to developing the bond between a person and society since it serves as their common ground.
According to Comte, society takes precedence over the individual and the family, giving sociology its focus. However, at the same time, social order develops into the fundamental direction of sociological imagination. The idea that there is something different from politics and economics that may be labeled “social” has led to the discussion of what sustains order in society within the evolutionary framework of development. The more people discuss this, the more it becomes evident. Therefore, understanding his opinions on the social circumstances under which he formed the law is crucial.
Features of Social Statics
A. The study of the circumstances and prerequisites of social order is referred to as social statics.
B. It focuses on the examination of significant institutions that maintain social order. For example, consider the family, which plays an essential role in the social system. It serves as the foundation for societal growth and social order.
C. It examines the society’s existing state, including its laws, regulations, and circumstances. Then, it looks at how these laws and regulations currently impact the community.
D. It looks at how the different parts of the social system work together and how they affect each other.
E. There are three tiers of society: the individual, the family, and the social group. The family is the fundamental social structure.
F. It is concerned with how society is currently constituted. Therefore, it refers to the current circumstances as it is being previewed.
G. It investigates topics related to societal order and stability.
Factors of Social Statics
Auguste Comte rejects the idea of seeing individuals as the foundation of society. It is incorrect to infer human social inclinations from his utilitarian concerns since doing so renders social states unachievable. Instead, he views the family as the fundamental and foundational unit of society and permits its downsizing to a couple if required. Family is the foundation of a social feeling that creates stability because it controls an individual’s egoistic tendency and helps him adapt to society.
Families are compared to elements in his theory of the collective body, groups and classes to tissues, and towns and cities to organs. Finally, Comte completed his arguments by asserting that language, religion, and the division of labor serve as society’s uniting or binding factors while also being aware of the limits of such analogies.
He identifies the three main constituents of stability: language, religion, and the division of labor.
A. Language
Language is vital for connecting community members because it is the “easiest and most prevalent form of communication.” Generational communication often takes place through language. It aids in passing on to the younger generations the knowledge and abilities of the older generation, giving them a foundation from which to advance. It is a method of preserving ideas and culture for future generations. It is impossible to achieve unity and social order without a shared language.
B. Religion
Religion serves as a “positive guide,” unifying society around a few core values, making up for the limitations of language. It keeps society together by upholding morality and preventing it from disintegrating due to individual differences. It serves as a behavioral guide and is the foundation of social order.
C. Division of Labor
Although work unites society based on the “similarity of classes,” it is believed that it would distance men from the general populace since they are more motivated by their interests than by the community. At this stage, men become more aware of their wants and flimsily connect them to societal demands. It fosters societal interconnectedness, so it is crucial for state collaboration and cooperation success.
Comte’s Implicit Model of Social Statics
Social systems become more distinct as they evolve, preserving their integration like all living things. With this understanding of the social organization, Comte came to the same issue that Adam Smith had first and forcefully raised: How is integration among components preserved despite growing functional differentiation?
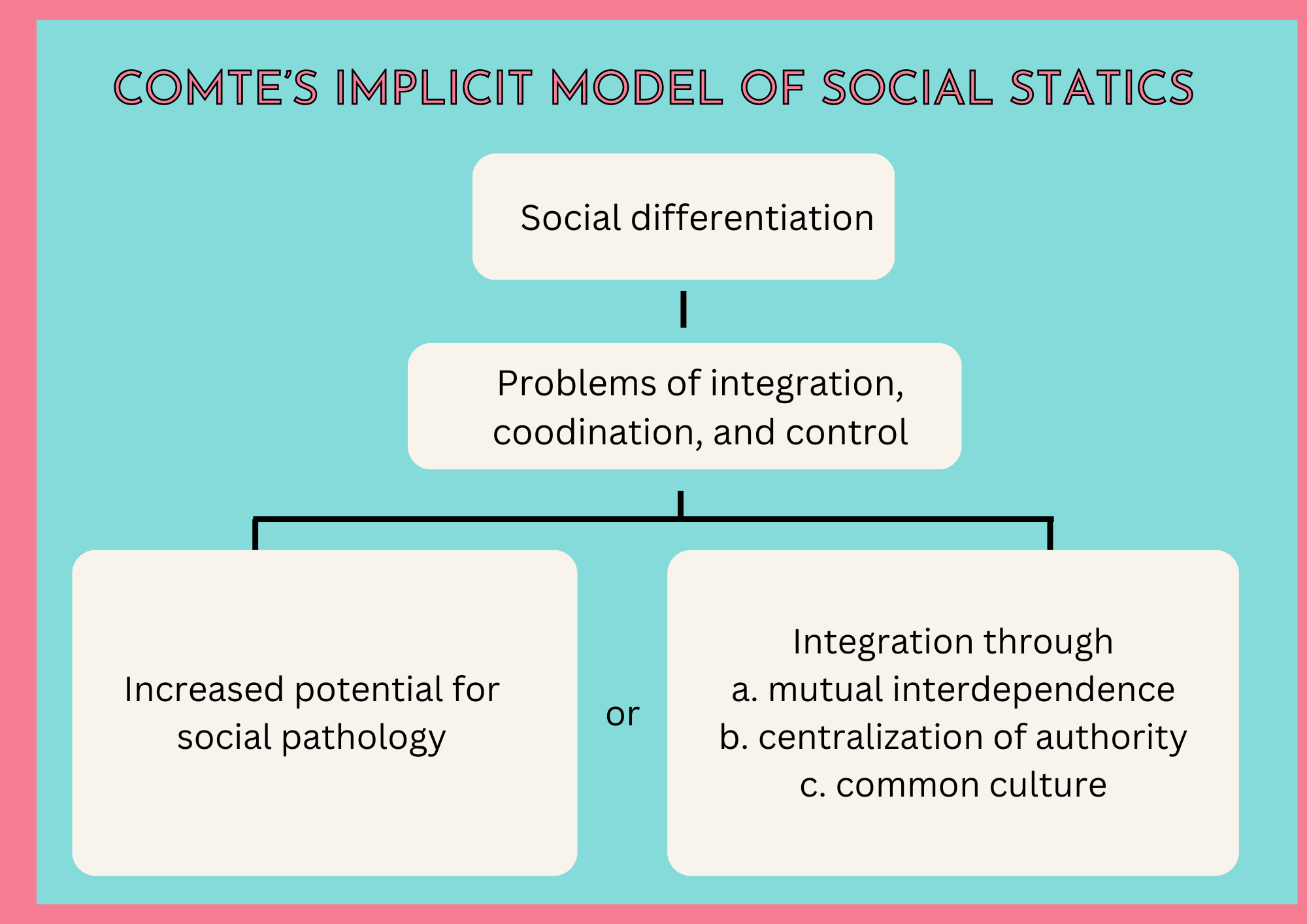
Comte’s suggested solution to this issue shows a lot about his perspective on the upkeep of social order.
First, the concentration of authority within the government mitigates the potentially destabilizing effects of social distinction, ensuring smooth coordination between system components.
Second, government efforts must go beyond the “material” and include the “intellectual and moral.”
Thus, the reciprocal reliance of system components on one another, the centralization of power to coordinate exchanges among elements, and the growth of a shared morality or spirit among population members all contribute to the maintenance of the human social structure.
Pathological states are more likely to develop to the degree that distinguishing systems cannot satisfy these requirements.
Comte claimed that by providing this analysis, he had discovered numerous laws of social statics because he held that preserving the social order was dependent upon divergence, the concentration of power, and the emergence of shared morality.
Although he did not go very far with his analysis, he gave Herbert Spencer and Emile Durkheim one of the fundamental theoretical issues in sociology and the general outline of the solution.
